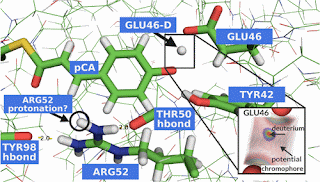
Almost three years ago I posted about the controversy concerning whether the photoactive yellow protein has low-barrier hydrogen bonds [for these the energy barrier for proton transfer is comparable to the zero-point energy]. I highlighted just how difficult it is going to be, both experimentally and theoretically to definitively resolve the issue, just as for an enzyme I recently discussed.
A key issue concerns how to interpret large proton NMR chemical shifts.
Two recent papers weigh in on the issue
The Low Barrier Hydrogen Bond in the Photoactive Yellow Protein: A Vacuum Artifact Absent in the Crystal and Solution
Timo Graen, Ludger Inhester, Maike Clemens, Helmut Grubmüller, and Gerrit Groenhof
A Dynamic Equilibrium of Three Hydrogen-Bond Conformers Explains the NMR Spectrum of the Active Site of Photoactive Yellow Protein
Phillip Johannes Taenzler, Keyarash Sadeghian, and Christian Ochsenfeld
I think the caveats I have offered before need to kept in mind.
As with understanding the active sites of most proteins the problem is that we don't have very direct experimental probes, but have to use indirect probes which produce experimental results that require significant modelling and interpretation.
I thank Steve Boxer for bringing one of these papers to my attention.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
A forgotten physicist: Amelia Frank (1906-1937)
In honour of International Women's Day, I bring to your attention a fascinating recent piece in The Conversation , Who was Amelia Frank?...

-
This week Nobel Prizes will be announced. I have not done predictions since 2020 . This is a fun exercise. It is also good to reflect on w...
-
Is it something to do with breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation? In molecular spectroscopy you occasionally hear this term thro...
-
Nitrogen fluoride (NF) seems like a very simple molecule and you would think it would very well understood, particularly as it is small enou...



No comments:
Post a Comment